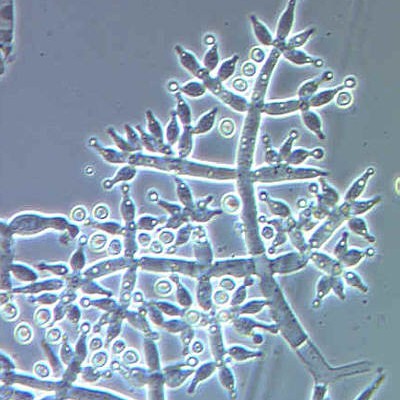
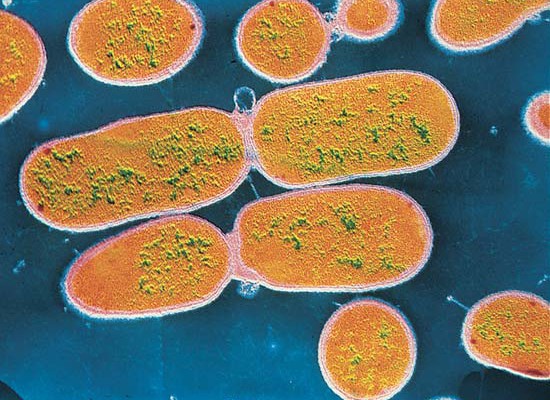
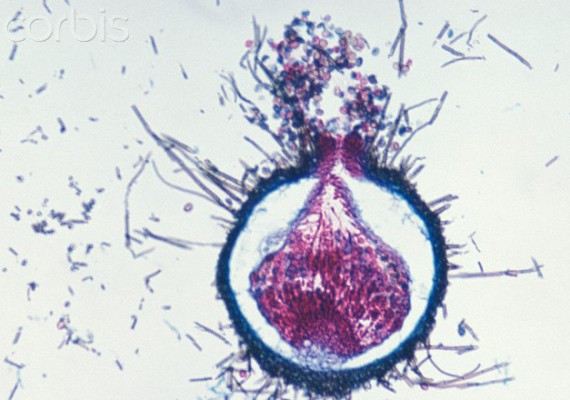
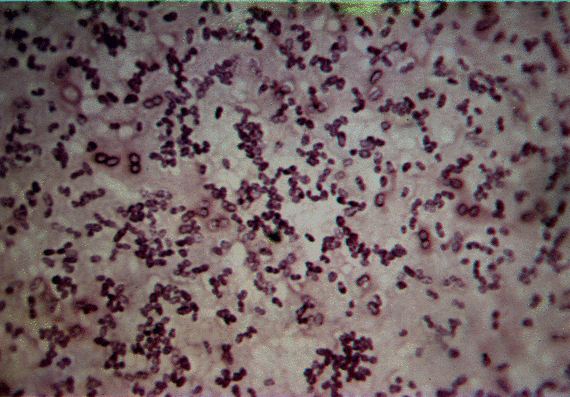
Bacillus is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped (bacillus) bacteria and a member of the phylum Firmicutes. Bacillus species can be obligate aerobes (oxygen reliant), or facultative anaerobes (having the ability to be aerobic or anaerobic). Ubiquitous in nature, Bacillus includes both free-living (nonparasitic) and parasitic pathogenic species. Under stressful environmental conditions, the bacteria can produce oval endospores that are not true 'spores', but to which the bacteria can reduce themselves and remain in a dormant state for very long periods.